Flexray Slots

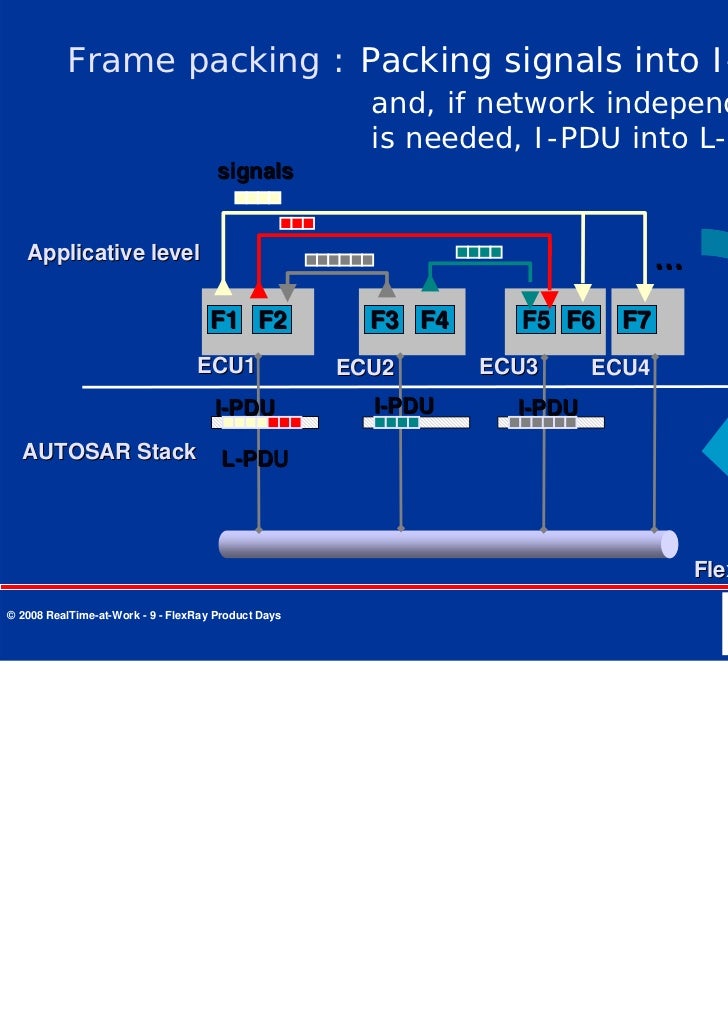
The problem model supported slot multiplexing, as defined in the FlexRay v3.0 protocol specification. Therefore, the main goal was to provide a schedule that satisfied FlexRay specifications and precedence relations between messages and minimized bandwidth usage. Figure 3: FlexRay communication cycle components (Source: Vector) Static Segment: organized into a number of time slots (static slots) of equal length.The FlexRay nodes affected to static slots. FlexRay cycle is composed of a defined number of such FlexRay frames. This cycle again is divided in a static segment, dynamic segment, a symbol window and a network idle time (NIT). The FlexRay frames in the static and the dynamic segment respectively are also known as slots. This leads to the structure shown in figure 4. In contrast to that, FlexRay supports TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access). Each device has a fixed time window (time slot), during which the device has exclu- sive access to the bus. These time slots are repeated in a fixed pattern.
The FlexRay protocol is a unique time-triggered protocol that provides options for deterministic data that arrives in a predictable time frame.FlexRay is a serial communication technology that is used in particular for data communication in very safety-critical use areas in the automobile.
Differential signaling on each pair of wires reduces the effects of external noise on the network without expensive shielding. FlexRay nodes typically also have power and ground wires available to power transceivers and microprocessors. FlexRay manages multiple nodes with a Time Division Multiple Access scheme. Every FlexRay node is synchronized to the same clock, and each nodes waits for its turn to write on the bus. Because the timing is consistent in a TDMA scheme, FlexRay is able to guarantee determinism or the consistency of data deliver to nodes on the network. This provides many advantages for systems that depend on up-to-date data between nodes.
- Static Segment
Reserved slots for deterministic data that arrives at a fixed period. - Dynamic Segment
The dynamic segment behaves in a fashion similar to CAN and is used for a wider variety of event-based data that does not require determinism.
Disadvantages of Flexray:
The bus has certain disadvantages like lower operating voltage levels and asymmetry of the edges, which leads to problems in extending the network length.
Ethernet may replace FlexRay for bandwidth intensive, non-safety critical applications.

The FlexRay protocol is a unique time-triggered protocol that provides options for deterministic data that arrives in a predictable time frame.FlexRay is a serial communication technology that is used in particular for data communication in very safety-critical use areas in the automobile.
Differential signaling on each pair of wires reduces the effects of external noise on the network without expensive shielding. FlexRay nodes typically also have power and ground wires available to power transceivers and microprocessors. FlexRay manages multiple nodes with a Time Division Multiple Access scheme. Every FlexRay node is synchronized to the same clock, and each nodes waits for its turn to write on the bus. Because the timing is consistent in a TDMA scheme, FlexRay is able to guarantee determinism or the consistency of data deliver to nodes on the network. This provides many advantages for systems that depend on up-to-date data between nodes.
- Static Segment
Reserved slots for deterministic data that arrives at a fixed period. - Dynamic Segment
The dynamic segment behaves in a fashion similar to CAN and is used for a wider variety of event-based data that does not require determinism.
Disadvantages of Flexray:
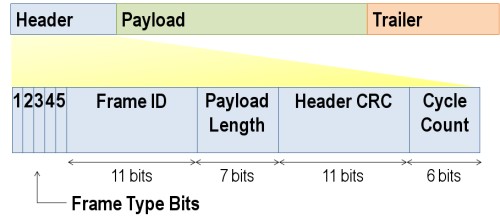
Flexray Slot
The bus has certain disadvantages like lower operating voltage levels and asymmetry of the edges, which leads to problems in extending the network length.
Flexray Slot Id
Ethernet may replace FlexRay for bandwidth intensive, non-safety critical applications.